Outcome 3 - Well-functioning markets
Output 3.1.1 Foreign investment policy advice and administration
Output 3.1.2 Financial system and corporate governance policy advice
Output 3.1.3 Competition and consumer policy advice
Output 3.1.4 Actuarial services
Output 3.1.5 Circulating coin and like products
Corporate services
Treasury provides advice to the Government on forming and implementing policy in support of well-functioning markets. Treasury's advice and other outputs help maintain and improve markets so investors and consumers can have confidence and certainty in making decisions that are well informed and free of market distortions and impediments. Treasury also provides the Executive for the Takeovers Panel and assists the Royal Australian Mint, a semi-autonomous Treasury division, with responsibility for producing circulating and numismatic coin for Australia, through representation on its Advisory Board.
Markets Group is responsible for providing advice on policy processes and reforms that promote a secure financial system and sound corporate practices, removes impediments to competition in product and services markets, and safeguards the public interest in matters such as consumer protection and foreign investment.
On 1 July 2002, Treasury was restructured. As a result, the performance information for Outcome 3 has been updated to reflect this new structure and varies from the 2002-03 Portfolio Budget Statements. The major changes are to include corporate governance policy advice, Takeover Panel and Axiss under Output 3.1.2 and rename Output 3.1.3 to competition and consumer policy advice to more aptly reflect the nature of the policy and the synergies within the outcome of well-functioning markets.
The performance information for the Royal Australian Mint, Output 3.1.5, has been reviewed since the release of the 2002-03 Portfolio Budget Statements to ensure it comprehensively covers the Royal Australian Mint's business in a balanced way, including the core business of providing circulating coin as well as its community service obligations.
In 2002-03, Markets Group, under Outcome 3, contributed to Government decisions and objectives through:
- providing advice on a range of issues including:
- prudential regulation of the financial sector;
- market access and pricing for the financial sector;
- structural reform matters, including those arising through the operation of the Government's competition policy;
- foreign investment policy including international investment matters and processing of foreign investment proposals;
- financial services and corporate regulation;
- consumer information and product safety issues to assist consumer participation in markets;
- professional actuarial services analysing and quantifying uncertain future financial flows for public sector clients;
- participating in international discussions strengthening international cooperation for the regulatory framework and promotion of Australia as a financial centre;
- consulting with other Australian Government agencies, State and Territory governments, industry, the general public and other stakeholders on various issues including coinage.
Figure 7: Outputs contributing to Outcome 3
Key priorities in 2002-03
Treasury's 2002-03 Portfolio Budget Statements and internal planning processes identified the following key priorities for Outcome 3:
- progress prudential supervision of financial institutions, including considering policy issues arising out of the HIH Royal Commission and options to improve the safety of superannuation;
- coordinate the Government's response to the independent review of the competition provisions (Part IV) of the Trade Practices Act 1974 and their administration;
- establish a scheme managed by a statutory authority, for temporary terrorism risk insurance cover until market coverage resumes;
- contribute to the World Trade Organisation and Free Trade Agreement negotiations with the United States;
- progress the Corporate Law Economic Reform Program through the review of audit regulation and corporate disclosure, taking into account developments overseas, and implementing resulting government decisions (CLERP 9) and reducing the paper compliance burden on Australian companies (CLERP 7);
- monitor the transition to the new system of financial services regulation, and consulting on and developing options for the compensation regime to support the new framework;
- consider market access and pricing issues, including a review of the cost and availability of public liability, medical indemnity and terrorism insurance;
- establish a Principles Based Review of the Law of Negligence; and
- provide policy advice to assist the Government on issues surrounding United Medical Protection and its wholly-owned subsidiary Australasian Medical Insurance Limited and provide a guarantee to the provisional liquidator for obligations for valid claims under current or past policies.
Key outcomes in 2002-03
- Treasury provided a submission to the HIH Royal Commission and provided advice to the Government on each of the Commissioner's 61 recommendations. Treasury implemented the major recommendations on the governance model for Australian Prudential Regulation Authority through the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Amendment Act 2003, and provided for the transfer of custody of certain records of the HIH Royal Commission to Australian Securities and Investments Commission through the HIH Royal Commission (Transfer of Records) Act 2003.
- Treasury provided the secretariat to the independent review of the competition provisions (Part IV) of the Trade Practices Act 1974 and their administration (Dawson Review). Treasury assisted in the development of the Government's response, and is currently working on its implementation, including through liaison with the States and Territories and Australian Competition and Consumer Commission.
- In response to the continued unavailability of terrorism risk cover for commercial property, Treasury developed the Terrorism Insurance Act 2003, which effectively deemed terrorism risk cover in certain insurance policies from 1 July 2003, and facilitated the creation of the Australian Reinsurance Pool Corporation. The Corporation is a statutory body, located in Canberra, which has the responsibility for the overall management of the Scheme.
- Australia concluded a Free Trade Agreement with Singapore in October 2002. Treasury is negotiating agreements with the United States and Thailand to further liberalise trade in services and investment.
- The Corporate Law Economic Reform Program (CLERP) reached some milestones during 2002_03. CLERP 7 legislation was introduced in December 2002 with effect from April 2003 to simplify document lodgement and compliance between Australian Securities and Investments Commission and its business clients. CLERP 8 (a model law on cross-border insolvency) and CLERP 9 (the effective regulatory and disclosure framework for corporations) discussion papers were released and consultations conducted.
- Treasury developed measures to facilitate transition to the new financial services regime to clarify the operation of the Financial Services Reform Act 2001 and address pra
ctical issues for industry transition. - Treasury developed the exposure draft of the Superannuation Safety Amendment Bill 2003, to improve the safety of superannuation.
- Treasury contributed to the Government's response to the increasing price and decreasing availability of public liability insurance. In line with the Government's response to the Review of the Law of Negligence, Treasury developed draft legislation to amend the Trade Practices Act 1974, which has been introduced into Parliament.
- Treasury, through the Medical Indemnity (Prudential Supervision and Product Standards) Act 2003, developed a prudential and product regulation framework for medical indemnity insurance. On 1 November 2002, Treasury transferred formal and administrative responsibility for the Government's guarantee commitments to United Medical Protection and Australian Medical Indemnity Insurance Limited to the Department of Health and Ageing.
- In December 2002, the Heads of the Australian Government, the States and the Northern Territory signed a revised Corporations Agreement with new constitutional arrangements.
- Treasury provided advice on product safety standards and managed the Consumer Information Program.
Other key outcomes in 2002-03 were:
- the Australian Government Actuary contributed to policy development through the provision of specialist actuarial and related advice to the Government and its departments and agencies;
- the Takeovers Panel continued to provide the mechanism for resolving disputes and raising the standards of market behaviour in takeovers;
- Axiss continued to promote Australia's attraction as a base from which to deliver financial services throughout the Asia-Pacific;
- the Royal Australian Mint continued to operate successfully in producing circulating and numismatic coins for Australia. Treasury undertook a review of the Mint's operating structures. Following on from the review, the Government provided funding through an appropriation to the Mint for the purchase of new capital equipment.
Table 4: Financial and staffing resources summary for Outcome 3
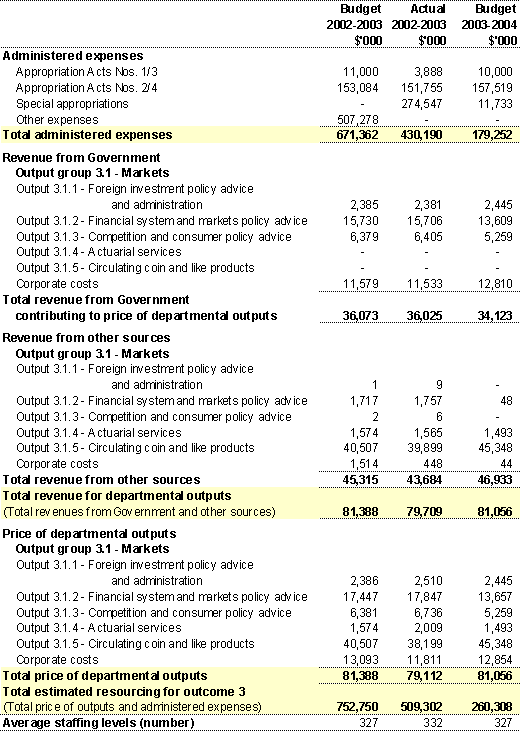
Note:
The Budget for 2002-03 is as per the 2002-03 Portfolio Additional Estimates Statements, any variations are due to internal reallocations.
The Actual for 2002-03 is as per the Audited 2002-03 Financial Statements.
The Budget for 2003-04 is as per the 2003-04 Portfolio Budget Statements (unless otherwise stated).
Output 3.1.1
Foreign investment policy advice and administration
The Foreign Investment Policy Division in Markets Group is responsible for the delivery of Output 3.1.1, foreign investment policy advice and administration.
Markets Group advises on foreign investment proposals, services the Foreign Investment Review Board, and makes decisions under staff authorisations consistent with policy. It also advises the Government on foreign investment policy as it relates to Australia's participation in multilateral and bilateral agreements on investment.
Performance information
Advice meets Treasury portfolio ministers' needs in fulfilling their responsibilities.
Proposals are processed efficiently to meet the needs of ministers, the Foreign Investment Review Board, foreign investors and their agents. Performance is currently regarded as satisfactory if:
- around 90 per cent of the roughly 5,000 proposals received each year are processed within 30 days of receipt of a completed application; and
- responses are provided, on average, within five days to around 40,000 general telephone and mail inquiries received each year.
Foreign investment policy is effectively disseminated and explained to achieve a high standard of applications and compliance with policy requirements, while minimising the proportion of foreign investment proposals requiring interim or final orders.
Implementation of an effective system of monitoring compliance with policy - possibly leading to prosecutions, but aimed at an overall reduction in non-compliance.
Government policy is appropriately represented and Australia's negotiating position is pursued effectively in international forums.
The OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises are effectively promoted, consistent with the responsibilities of the National Contact Point for the Guidelines.
Analysis of performance
Advice and input into policy processes
During 2002-03 Treasury and the Foreign Investment Review Board provided advice to portfolio ministers on larger, more important or sensitive foreign investment cases requiring ministerial decisions against associated legislation and policy. Significant cases such as Xstrata Plc's acquisition of MIM Holdings Limited, Burns, Philp & Company Limited's takeover of Goodman Fielder Limited and Constellation Brands Inc's purchase of BRL Hardy Limited were referred to the Treasurer, or a ministerial delegate for a decision. However, Treasury officers under delegation reviewed most cases, with senior management and the board overseeing those decisions on a weekly basis for consistency of process and policy.
Representation in international forums
Treasury provides policy input into international investment issues in multilateral forums, such as the World Trade Organisation and OECD, in regional forums such as Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), and bilaterally through free trade agreements, investment protection and promotion agreements and other bilateral partnerships.
Free Trade Agreements/Closer Economic Cooperation
As noted in Output 1.1.2, Treasury is negotiating free trade agreements with the United States and Thailand to further liberalise trade in services and investment. Australia concluded a Free Trade Agreement with Singapore in October 2002. High-level consultations between Australia and Japan to explore options for deeper economic links have similar objectives. Treasury provides expert advice on the impact of, and implications for, Australia's foreign investment policy regime.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Treasury promotes compliance with the OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises. The guidelines recommend responsible business conduct by multinational enterprises operating in or from the 30 OECD member countries, and other adhering countries, in employment and industrial standards, disclosure, the environment and bribery. Compliance is voluntary.
Each adhering country has a national contact point to ensure effective implementation and promotion of the guidelines. The General Manager of the Foreign Investment Policy Division is the Australian national contact point. In 2002-03, the focus was on four main outcomes:
- finalising the national contact point's structure and refining procedures for handling specific instances of Australian adherence to the guidelines;
- continuing the constructive dialogue established with stakeholders and engaging interested parties on key issues arising from implementing the guidelines;
- initiating outreach to Australia's top 100 companies to promote the guidelines;
- enhancing promotional efforts through developing a new website www.ausncp.gov.au and increasing efforts to incorporate the guidelines into domestic corporate governance and social responsibility reporting frameworks.
At the annual meeting in June, the national contact point tabled a detailed report (prepared in consultation with business, labour and other non-government organisations) on its activities during t
he year and attended an OECD Roundtable on the role of the guidelines in tackling corruption.
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
During 2002-03, Treasury revised and updated the investment chapter of the annual APEC Individual Action Plan. Australia's plan was subject to peer review and received very positive feedback.
Liaison with Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade
Treasury provides expert advice to Foreign Affairs and Trade on Australia's involvement in the World Trade Organization Working Group on Trade and Investment. In 2002-03 the working group examined the nature, scope and operational characteristics of proposed multilateral rules on investment, including modalities for negotiation.
Treasury also provides expert advice to Foreign Affairs and Trade on Australia's negotiation of bilateral investment treaties. These Investment Protection and Promotion Agreements promote the international flow of capital for economic activity and development. A model Australian text provides the basis for negotiating these agreements. Australia is close to completing new investment treaties with Mexico and Turkey.
Processing of proposals
Treasury considered about 5,400 proposals in 2002-03, around 10 per cent more than in 2001-02. About 94 per cent of cases were decided within 30 days of receipt of sufficient information. Treasury also responded to thousands of telephone inquiries and written and email inquiries, generally within five days. During the year, 153 final, interim or divestment orders were issued, mainly for real estate. While a similar number of orders were issued last year, this is a smaller proportion of the overall number of cases, an encouraging outcome in terms of continuing efforts to improve compliance.
Compliance standards
Treasury's efforts through 2002-03 to strengthen compliance focused on three broad elements:
- developing a new case management system and integrated online application facility to improve application accuracy and reduce processing times; and
- enhancing communication of the requirements of foreign investment policy to foreign investors and their agents, involving a continuing program of targeted public speeches, the redesign of the Foreign Investment website and the development of easy-to-follow written materials:
- the Urban Land Policy was redrafted in 2002-03, with other policy statements due to be redrafted in 2003-04;
- a review of the telephone answering system for handling inquiries was completed; and
- a rolling program of monitoring compliance with foreign investment policy. Treasury examined around 1,500 decided proposals in 2002-03, particularly in the real estate sector, to ensure fulfillment of conditions. In some instances, this resulted in punitive action against foreign parties.
Output 3.1.2
Financial system and corporate governance policy advice
The Financial System Division and former Corporate Governance Division (now incorporated into the Corporations and Financial Services Division) in Markets Group, together with the Takeovers Panel and Axiss Australia, were responsible for the delivery of Output 3.1.2, financial system and corporate governance policy advice.
Markets Group contributes to Outcome 3, well-functioning markets, by providing advice to Treasury ministers on financial system and financial market operation, including market integrity and investor protection, company law and corporate governance issues, corporate insolvency, corporate financial reporting, the responsible portfolio agencies and currency. Markets Group, through Axiss Australia, implemented the program to develop Australia as a global financial centre.
Performance information
Advice meets Treasury portfolio ministers' needs in administering their responsibilities and implementing government decisions as they relate to financial system and markets issues.
Effective presentation of relevant information to inform public debate.
Statutory and other procedural requirements are met.
Secretariat services provided to advisory bodies are effective.
Representation and/or liaison by Treasury officers with other agencies, private sector organisations and international bodies, is assessed by participants as effective.
Implementation of Axiss Australia program achieves intended results.
The Takeovers Panel achieves intended results.
Analysis of performance
Treasury provided advice and program support to Treasury portfolio ministers, and engaged with other agencies on issues relating to financial institutions and markets; development of Australia as a financial centre; and issues concerning corporate disclosure, governance and insolvency. Treasury also processed related ministerial correspondence, published relevant information and ensured other procedural requirements were met, provided effective support services to advisory bodies, liaised and consulted with stakeholders and represented the Australian Government at various meetings.
Financial system
Response to the collapse of the HIH Group
During 2002-03, Treasury provided policy advice to ministers and oversaw management agreements relating to the HIH Support Scheme.
In October 2002, Treasury provided a submission to the HIH Royal Commission. The Government tabled the report of the HIH Royal Commission on 16 April 2003. Treasury provided advice on each of 61 policy recommendations covering corporate governance and financial reporting, governance arrangements and internal processes for the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority and the regulation of general insurance.
Treasury was instrumental in implementing the major recommendations on the governance model for the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority through the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Amendment Act 2003 (the APRA Amendment Act), which received Royal Assent on 19 June 2003. The APRA Amendment Act achieved a number of major objectives, including replacing the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority part-time board with a full-time executive group, clarifying its role within the financial system, enhancing its disclosure and conflict of interest framework, and clarifying its relationship with other agencies.
The commissioner identified 56 possible breaches of the Corporations Act 2001 and the Crimes Act (NSW) 1900. The Government has referred those matters to the Australian Securities and Investments Commission or, in a small number of cases, to the New South Wales Director of Public Prosecutions. To overcome potential procedural impediments, Treasury prepared the HIH Royal Commission (Transfer of Records) Act 2003, which provides for the transfer of custody of certain records of the HIH Royal Commission to the Australian Securities and Investments Commission.
Medical indemnity reform
Treasury continued to provide advice on developing and implementing the Government's package of medical indemnity reforms. Treasury was responsible for the Medical Indemnity (Prudential Supervision and Product Standards) Act 2003, which established a prudential and product regulation framework for medical indemnity insurance. As with all package components, the Act was the subject of detailed consultations with medical indemnity providers and doctors' groups. Treasury also provided advice on doctors' personal exposure to liability payouts and provision of indemnity cover for retired medical practitioners.
On 1 November 2002, Treasury transferred responsibility for the Government's guarantee commitments to United Medical Protection and Australian Medical Indemnity Insurance Limited, to the Department of Health and Ageing.
Australian Reinsurance Pool Corporation
Following continued unavai
lability of insurance risk cover for commercial property in relation to acts of terrorism, Treasury provided advice to ministers on a reinsurance scheme after consulting with stakeholders, including banking, property and insurance industry representatives. The resultant Terrorism Insurance Act 2003 effectively deems terrorism risk cover into certain insurance contracts from 1 July 2003. Treasury presented a speech on terrorism insurance to the Insurance Council of New South Wales Conference and to the third International Conference for Emerging Insurance Markets, in Delhi.
Public liability and professional indemnity insurance
On public liability and professional indemnity insurance, Treasury provided policy advice and support for three ministerial meetings, provided policy advice on action to take in response to premium increases, and worked with the States and Territories through the Insurance Issues Working Group.
Treasury also provided effective secretariat services to the Principles Based Review of the Law of Negligence, chaired by Justice David Ipp.
Financial services reform
Treasury has responded to issues arising out of the implementation of the Financial Services Reform Act 2001 (FSR Act). The FSR Act is a harmonised licensing, conduct and disclosure regime for financial products, markets and service providers. In cooperation with the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, industry and consumer stakeholders, Treasury is working to ensure that transition to the new regime by 11 March 2004 is as smooth as possible. Treasury developed the Financial Services Reform Amendment Bill 2003, introduced to Parliament on 26 June, to clarify the operation of the FSR Act and remove practical difficulties encountered during transition. In addition, Treasury has instructed on the development of several sets of corporations regulations. In keeping with the Government's Corporate Law Economic Reform Program processes, consultation on proposals for legislative and regulatory changes has been extensive.
Payments system reform
Treasury assisted the Reserve Bank of Australia in implementing reforms to the Australian Payments System regarding credit cards. Treasury consulted with industry stakeholders on drafting regulations and provided advice to portfolio ministers on the progress of the reforms, and on responses to public concerns. Treasury provided documents, under the Freedom of Information Act 1982, in response to a request from MasterCard Australia.
Superannuation
Subsequent to the response to the Superannuation Working Group's final report into options to improve the safety of superannuation, Treasury provided advice on developing the exposure draft of the Superannuation Safety Amendment Bill 2003. The Bill amends the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 (SIS Act) in line with the recommended reforms.
In response to the Superannuation Working Group's recommendations, the Government announced that Treasury would review the compensation arrangements under Part 23 of the SIS Act to grant financial assistance to Australian Prudential Regulation Authority regulated superannuation funds that suffer losses as a result of fraudulent conduct or theft. These grants are conditional, including the loss must have led to a substantial diminution in the fund leading to difficulty in paying benefits. Grants to superannuation funds that suffered loss through fraudulent conduct or theft totalled $27 million during 2002-03.
Financial Sector Levies review
Treasury chaired a review of financial sector levies to evaluate arrangements to determine levies imposed on the financial services sector to support the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority's operations, and certain operations of the Australian Securities and Investment Corporation and the Australian Taxation Office.
International liaison
Treasury continued work with other portfolio agencies and key stakeholders to expand Australia's links to regional and global financial markets. Treasury officers liaised with their New Zealand and Singaporean counterparts on mutual recognition of cross-border offerings of securities.
Treasury participated in the Financial Action Task Force workshop meetings on money laundering and consulted extensively with the Australian financial sector. Treasury was represented at OECD Insurance Committee meetings and provided advice to the OECD on flood mitigation, claims management, corporate governance for insurers and terrorism cover.
Trade in financial services
Treasury provided support for negotiations on financial services for the free trade agreements with Singapore and the United States, and the Doha Round of the World Trade Organization.
Takeovers Panel
The Takeovers Panel is the primary forum for resolving disputes that arise during a takeover. Treasury advises portfolio ministers on panel operations and appointments. During 2002-03, the panel dealt with 40 applications under Part 6.10 of the Corporations Act including five internal reviews and three reviews of decisions by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission. No panel decision was subject to external review.
Currency
Treasury chaired and served on the Royal Australian Mint Advisory Board during the year. In 2002, Treasury reviewed the Mint's operations. As a result of the review, the Government has approved the funding to enable the Mint to purchase new capital equipment.
Treasury also prepared currency determinations for the Perth Mint's numismatic coin programs.
Company law and corporate governance
Corporate Law Economic Reform Program 9
This project seeks to ensure Australia has an effective regulatory and disclosure framework for corporations, improving the structures and incentives for a fully informed market. In September 2002, Treasury ministers released a discussion paper canvassing options to improve audit and corporate disclosure practices in Australia, as well as analyst independence and shareholder participation. It attracted over 60 submissions. Treasury consulted the Business Regulation Advisory Group on the proposals and is expected to release draft legislation in late 2003 for consultation.
International corporate governance
Treasury led the establishment of the APEC Pathfinder Initiative on corporate governance and disclosure regimes. The initiative is designed to raise awareness of and promote improvements in corporate governance frameworks in the region, and is expected to report in 2004. Treasury also led a review of the OECD Principles of Corporate Governance by the OECD Steering Committee on Corporate Governance.
Corporate Law Economic Reform Program 7
Treasury assisted the Government to introduce and pass legislation to streamline the relationship between the Australian Securities and Investments Commission and its business clients by simplifying document lodgment and compliance. The Corporations Legislation Amendment Act 2003, the Corporations (Fees) Amendment Act 2003 and the Corporations (Review Fees) Act 2003 were passed on 27 March 2003 and generally took effect from 1 July 2003.
Corporate Law Economic Reform Program 8
Treasury published the proposals on adopting the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) Model Law on cross-border insolvency for public comment in September 2002. Most submissions favoured adopting the model law, which is likely to be enacted in a Bill to be introduced in 2004.
Through contributing to the working group on insolvency law of the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law, Treasury provided input on developing a set of legislative guidelines for domestic insolvency frameworks. This work is expected to be completed in 200
4.
Directors' bonuses
Treasury advised on the development of the Corporations Amendment (Repayment of Directors' Bonuses) Act 2003, which took effect from April 2003 and permits liquidators to reclaim unreasonable payments by a company to directors in the lead-up to insolvency.
Statutory and other procedural requirements
Ministerial decisions under statutes
Under the Corporations Act 2001, portfolio ministers have a significant role in ensuring market integrity. Treasury provided ongoing policy advice in relation to ministerial powers to disallow the operating rules of markets and clearing and settlement facilities and approve new market applications.
Treasury provided ministers with advice and Treasury officers prepared instruments to authorise individual financial institutions under the Financial Sector (Shareholdings) Act 1998 and the Banking Act 1959.
Appointments
Treasury processed appointments to the Financial Reporting Council, Australian Prudential Regulation Authority, the Payments System Board, the Superannuation Complaints Tribunal, the Australian Accounting Standards Board, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, the Companies Auditors and Liquidators Disciplinary Board, the Takeovers Panel, the Financial Sector Advisory Council, the Australian Reinsurance Pool Corporation Board, the Corporations and Markets Advisory Committee and its legal subcommittee.
Secretariat services
Treasury provided secretariat services to the Ministerial Council for Corporations, which met three times during 2002-03. In December 2002, the Heads of the Australian Government, the States and Northern Territory signed a revised Corporations Agreement, which supports the Ministerial Council and provides the political underpinning for the new constitutional arrangements supporting the Corporations Act 2001.
Treasury provided secretariat support for the Financial Reporting Council, a stakeholder body that provides broad oversight of the accounting standard setting process, including the Australian Accounting Standards Board.
Treasury provided secretariat services to the HIH Assistance Review Panel and the Financial Sector Advisory Council.
Axiss Australia
Throughout 2002-03, Axiss focused strongly on the promotion and development of Australia's funds management sector. The size of the pool of funds (currently in excess of $600 billion and the fifth largest in the world) and projections for growth make it especially attractive to global firms.
Among the firms that Axiss assisted was Mellon Financial Corporation, one of the world's largest asset managers. Assistance included building a business case to support the firm's establishment in Australia and addressing queries regarding the structure of the local investment industry. Axiss undertook a marketing mission to New York and Washington DC in February and held bilateral meetings with senior representatives of global investment banking and asset management firms, including Citigroup, Lehman Brothers and Goldman Sachs.
Axiss met with key executives from leading private equity and hedge fund firms such as Bear Stearns, Credit Suisse Asset Management and Tremont Advisors and international delegates from the World Council of Credit Unions.
Axiss submitted to the Board of Taxation's review of Australia's international taxation arrangements that aspects of the foreign investment funds and capital gains tax regimes impede the expansion of domestic operations and regional businesses from Australia.
Axiss launched finance@work in May 2003 so Year 11-12 students can spend a minimum of one week in a financial services organisation, undertaking structured tasks focused on work skills, money management and career planning. In November 2002, Axiss led a mission to China to showcase Australia's excellence in finance education and training. The mission visited Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen, and gave presentations to more than 200 representatives from government, regulators and finance industry participants.
Another of its education initiatives, the Axiss Scholar Program, has provided work experience for 55 tertiary-level students and generated over $560,000 in scholarship funds.
In June 2003, Axiss hosted the third APEC Future Economic Leaders Think-Tank in Sydney to encourage cooperative approaches to financial issues in the APEC region. The four-day event gathered together future `influencers' of economic policy.
In June 2003, the Government announced that, from 1 July, Axiss would operate as a division of Invest Australia, the national inward investment agency. As a result, Axiss has transferred from Treasury to the Department of Industry, Tourism and Resources. It will retain its brand name and continue to provide the Treasurer with six-monthly reports on its activities.
Output 3.1.3
Competition and consumer policy advice
Competition and Consumer Policy Division was responsible for the delivery of Output 3.1.3, competition and consumer policy advice.
Markets Group contributed to Outcome 3 by providing advice on policy issues and the legislative framework for the development and operation of competition and consumer policy, and markets more broadly. This advice included the areas of the competition and consumer provisions of the Trade Practices Act 1974 and the Prices Surveillance Act 1983 and structural reform of key sectors of the economy, including those providing essential infrastructure.
Performance information
Advice meets Treasury portfolio Ministers' needs in discharging their responsibilities under legislation and in implementing government decisions in relation to competition and consumer policy.
Statutory and other procedural, administrative and reporting requirements are met.
Effective representation and/or liaison with other agencies, private sector organisations and international bodies to promote competitive, efficient and well-informed markets.
Effective presentation of relevant information to inform consumers and businesses.
Secretariat services provided to advisory bodies are effective.
Progress in providing effective and relevant consumer information and mechanisms to promote consumers protection in areas of product safety and support effective self-regulation in the marketplace.
Analysis of performance
Competition policy
During 2002-03, Treasury provided advice to Ministers on reviews that recommended amendments to Australia's competition framework and progressed their implementation.
An independent review of the competition provisions (Part IV) of the Trade Practices Act 1974 and their administration (Dawson Review) was undertaken in 2002-03, supported by a secretariat located in Treasury. On 16 April 2003, the Treasurer released the Dawson Review and the Government's response. The response endorsed the Review, and accepted recommendations aimed at improving the competition and authorisation provisions, and administration of the Trade Practices Act. Treasury assisted with the Government's response, and is developing its implementation, in consultation with the States and Territories and Australian Competition and Consumer Commission.
Treasury also finalised or progressed Government responses to the Productivity Commission's reviews into the Prices Surveillance Act 1983 (including repeal and amendment of legislation); and section 2D (local government exemptions) and Part IIIA (National Access Regime) of the Trade Practices Act 1974.
Treasury has an advisory, reporting and coordination role in the Australian Government's implementation of the national competition policy. Treasury provided advice to ministers on NCP payments to th
e States and Territories, sector specific reforms and inter-jurisdictional issues during 2002-03. Treasury also oversights the preparation and publication of the Australian Government's NCP annual report, which details the Government's performance and operation in relation to its national competition policy obligations.
Treasury provided guidance on competition review and reform issues to other departments and agencies, in conjunction with the Office of Regulation Review of the Productivity Commission. The Commonwealth Legislation Review Schedule outlines the reviews of existing Australian Government legislation that restricts competition or imposes costs or confers benefits on business. In 2002-03, six legislation reviews listed were finalised, some in conjunction with other portfolios, and one review commenced.
Treasury worked closely with the Department of Finance and Administration to update the Commonwealth Competitive Neutrality: Guidelines for Managers. The revised guidelines will be published in 2003-04.
Treasury advice on structural policy covered a wide range of issues. Treasury prepared policy advice on issues affecting the electricity and natural gas markets, including proposed changes to the structure and operation of Australia's national energy market following the release of the Council of Commonwealth Independent Review of Energy Market Directions Report in December 2002.
Treasury's policy advice on transport markets focused on land transport including the Government's AusLink proposals and arrangements for interstate rail transport. Treasury also advised on developments in the aviation sector, in particular, on evolving competitive pressures, and on the airports economic regulatory regime in the context of the international downturn in aviation.
Treasury coordinates and advises on the preparation of terms of reference for research and inquiries by the Productivity Commission. In 2002-03, the Government provided five public inquiries and five commissioned research references to the Productivity Commission.
Treasury had extensive dealings with other agencies, private sector organisations and international bodies to promote competitive, efficient and well-informed markets. In 2002-03, Treasury also dealt with a large volume of correspondence relating to competition and consumer policy.
Treasury contributed to the development of competition and regulatory frameworks in OECD member and non-member countries, through involvement in the OECD's competition committees. Treasury made contributions in the areas of competitive neutrality and regulatory policy.
Treasury has contributed actively to Australia's participation with the work of the World Trade Organisation to realise a multilateral competition framework agreement as part of the Doha Round, participating in discussions and informing World Trade Organisation members of Australia's experiences in the development of competition law and policy.
Treasury has also been involved in negotiating competition chapters in free trade agreements with Thailand, Singapore and the United States of America, and in supporting the Australia-Japan trade and economic consultations.
Consumer policy
Treasury provided advice to the Government on regulatory frameworks that support consumer confidence and help consumers actively participate in the market.
In December 2002, the Trade Practices Amendment Act (No 1) 2002 received Royal Assent. This redrafted the sections on the prohibition of pyramid selling in plain English.
The Trade Practices Amendment (Liability for Recreational Services) Act 2002 was also passed by Parliament in December 2002, to permit participants in inherently risky activity to waive their rights to sue for breach of the contractual condition implied by section 74 of the Trade Practices Act 1974. Without this amendment, the public liability insurance crisis could have caused many recreational service suppliers to cease providing services.
Treasury also continued to participate in international consumer policy meetings. In particular, Treasury hosted the 65th session of the OECD Committee on Consumer Policy, which finalised the OECD Guidelines for Protecting Consumers across Borders from Fraudulent and Deceptive Commercial Practices. These guidelines, launched in June 2003, outline a framework for cooperation between enforcement agencies to protect consumers against the growing problem of cross-border fraud and deceptive practices.
In December 2002, the Parliamentary Secretary to the Treasurer re-appointed an Expert Group of leading industry and consumer professionals to advise him on consumer policy in e-commerce. Treasury continued to provide secretariat support to the Expert Group.
Treasury provided secretariat support to the Ministerial Council on Consumer Affairs and government consumer advisory bodies. The Council comprises Australian Government, State, Territory and New Zealand Ministers responsible for consumer policy and legislation.
Treasury also provided the secretariat for the Commonwealth Consumer Affairs Advisory Council. This Council advises the Parliamentary Secretary to the Treasurer on current and emerging consumer policy issues, and in 2002-03 released Consumer Issues and Youth, a research report examining consumer issues affecting young Australians.
Consumer safety
Treasury provided advice on product safety standards including bunk beds, on product bans including children's dart gun sets, and possible hazards with the use of liquid filled yo-yo balls.
Treasury oversaw, monitored and assessed the effectiveness of over 800 safety-related voluntary product recalls, in conjunction with other Australian Government and State authorities.
Treasury also participated in the work of the Standards Australia Technical Committees developing and updating standards as well as developing a national coronial database.
Treasury continued to work closely with Standards Australia, industry organisations and State and Territory Governments to promote safer markets and worked closely with New Zealand and the States and Territories to harmonise consumer safety regulation under the Trans-Tasman Mutual Recognition Arrangement.
Consumer information
Treasury manages the Consumer Information Program to promote greater national consistency in providing information to consumers and addressing areas of identified consumer need. Key elements include:
- offline centralised referral through The Australian Consumer Handbook;
- online centralised referral through www.consumersonline.gov.au;
- information targeting consumer scams through The Little Black Book of Scams and www.scamwatch.gov.au;
- product safety information initiatives; and
- resources to assist consumers shopping online, for example the release of free consumer software to help those shopping on the internet www.consumerping.gov.au
Output 3.1.4
Actuarial services
The Australian Government Actuary is responsible for the delivery of Output 3.1.4, actuarial services.
The Australian Government Actuary provides, on a fee-for-service basis, accurate and timely actuarial and related advice to the Government and its departments and agencies.
The office also has an ongoing support role in Treasury policy issues with an actuarial component.
Performance information
Efficient provision of high quality professional services, with income from consultancy fees relative to total costs meeting specified quantitative criteria.
Analysis of performance
The Australian Government Actuary operates in a competitive and contestable market
for actuarial services. Income from consultancy services relative to total costs is, therefore, a primary indicator of performance. The Australian Government Actuary operates a special account to ensure its financial operations are managed properly and transparently. At 30 June 2003 the account was in a sound financial position.
Actuarial advice should be of the highest quality. The absence of any complaints about the quality of professional services indicates strong performance.
Consultancy services
Australian Government Actuary consultancy services typically involve analysing uncertain future financial flows using financial modeling techniques, documenting the analysis, and presenting the results to clients.
Departments which sought advice included Defence; Attorney-General's; Education, Science and Training; Family and Community Services; Health and Ageing; and Veterans' Affairs. Centrelink and the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority also sought advice.
Feedback from these agencies indicates that they were generally very satisfied with the advice received, and its value as an input to achieving their objectives.
A structural increase in Centrelink case workload over the course of the year put pressure on turnaround times. This was addressed and largely resolved by the end of the year.
Services to Treasury
The Australian Government Actuary contributed its technical expertise on a range of policy issues, including medical indemnity arrangements, the superannuation system and insurance matters.
Treasury provided funding for this work which accounted for around 10 per cent of the office's total revenue for the year.
Operational outcomes
The office operates under the direction of an internal management board comprising three senior Treasury officers, including the Australian Government Actuary. This board reviews financial performance and oversees the strategic direction of the office.
Output 3.1.5
Circulating coin and like products
The Royal Australian Mint is a semi-autonomous operating division of the Treasury, responsible for producing circulating and numismatic coin for Australia. The Mint also produces a range of high quality collector coins together with minted non-coin products including medallions. The Mint's collector coin and minted non-coin business is commercial, within government-set parameters. In 2002-03 the Mint received no direct budget funding.
Performance information
Advice meets Treasury portfolio ministers' needs in administering their responsibilities and implementing government decisions as they relate to coinage and Royal Australian Mint operations.
Produce circulating coin to Reserve Bank of Australia forecasts.
Meets financial performance targets.
Maintain the National Coin Collection and the Royal Australia Mint's visitors gallery, and promote public understanding about the cultural and historical significance of coins.
Analysis of performance
Treasury and the Royal Australian Mint provided advice on a range of currency related matters including coin designs.
2002-03 was another challenging year for the Mint in managing the business in uncertain times. Despite exchange rate swings and cautious customer spending, the Mint operated with a sound profit.
The Mint's operating profit before company tax and net of seigniorage was $1.893 million. The profit before tax represents a return on gross assets, excluding the Coin Museum and approved excess circulating coining inventory of 11.02 per cent.
The Mint returned $80.242 million to consolidated revenue in seigniorage, royalties and other payments.
Inventory holdings decreased from $17.22 million in 2001-02 to $15.42 million in 2002-03 due to decreased holdings of finished circulating coin and raw material blanks.
The Mint made a concerted effort to control discretionary expenditure, reducing it to $12.98 million from $13.8 million in 2001-02. Expenditure is 32.7 per cent of revenue.
Sales of corporate and other product was $2.01 million for the year. This includes the sales of foreign coin production orders of $0.608 million for New Zealand, Fiji and the Cook Islands. Sales of medals, medallions and tokens to government and the corporate sector remains a highly competitive market.
Demand for circulating coin was lower than previous years (Tables 5 and 6). The Reserve Bank of Australia purchased 238 million coins in 2002-03, compared to 544 million coins the previous year. This should allow the banking system to absorb surplus coins that have accumulated. These surpluses arose from prudent purchases to mitigate the risk of uncertainty during the Y2K calendar transition, and ownership transfer of coin pools to commercial banks.
The drop in demand for all denominations of circulating coin reduced seigniorage earnings from $129.538 million last year to $79.656 million this year.
The Mint's numismatic program yielded $17.961 million. The Mint has divided collector coin issues into two broad categories. Products such as the year sets, baby sets and wedding sets are purchased both by serious and occasional coin collectors and are produced in unlimited or very large numbers. More numismatic products have limited mintages and the coins generally are available only from the Mint and coin dealers (with numismatic knowledge and who sell and buy back coins).
This results in many numismatic coin issues selling out, some in near-record times. In 2002-03 the following issues sold out: the $1 silver proof coin commemorating the end of the Korean War, the fine proof silver 2003 year set, the proof Rugby World Cup coin, the selectively gold plated silver kangaroo, the hologram coin, and the $10 proof commemorative `Adelaide Pound' coin. As a result, many coins and coin sets issued over the past few years are in considerable demand, reinforcing the interest in current new issues of both the numismatic and generally available coins.
Sales to overseas dealers reached a very high level with coins having an overseas interest with Australian themes. These included the Battle of Sunda Strait, Masterpieces in Silver and Accession coins.
For the second year in a row, the Mint has won a prestigious international `Coin of the Year' award by United States based Krause Publications. The design, an Aboriginal interpretation of the kangaroo, was commissioned from the Aboriginal artist Jeanette Timbery.
The Mint also uses collector coin issues to highlight Australia's numismatic and general history. Modern day issues featuring historic `icon' coins can re-ignite interest in the older coin issues. Two modern issue coins featuring historic Australian coins were the $10 Commemorative Numismatic of the Adelaide Pound and the Subscription Coin of the Holey dollar and dump.
Other coins issued this year commemorating Australian culture and history were the $1 proof silver kangaroo coin with the kangaroo designed by Aboriginal artist Ray Thomas; the $1 aluminium bronze paying tribute to Australia's Vietnam veterans and $1 proof silver coin commemorating the fiftieth anniversary of the end of the Korean War. The Masterpieces in Silver set highlighted Australia's nautical history with the depiction of four historic sailing vessels. The Golden Jubilee of the Coronation of Queen Elizabeth II was commemorated on two precious metal collector coins. Possibly the most topical highlight was the theme of the 2003 proof and uncirculated year sets saluting Australia's volunteers.
The Mint also launched a design competition for primary school pupils to produce a design for a 50c coin. The winning designer will win $10,000 for their school.
After strong support during the Olympic and Centenary of Federation years, visit
s to the Mint's visitors gallery weakened, reflecting a general decline in tourist activity throughout the region (Table 7).
Large numbers of school children visit the Mint so the cafeteria has been converted into an additional viewing room for the Mint video. This should greatly relieve congestion. At the Mint's first Open Day on Saturday 29 March 2003, visitors were escorted through the factory area and allowed close to the operating circulating coin presses. Mint staff acted as guides and a collection supported the Canberra Bushfire Relief Fund.
As part of the Coin Disposals and Acquisition Program, a set of 1916 proof coins was sold at public auction. Proceeds will be used to make strategic purchases of coins for the National Coin Collection.
Table 5: Australian decimal coin issued by Treasury
| Year | $2 | $1 | 50c | 20c | 10c | 5c | 2c | 1c | Total |
| $'000 | $'000 | $'000 | $'000 | $'000 | $'000 | $'000 | $'000 | $'000 | |
| 1965-92 | 395,960 | 319,780 | 217,625 | 161,303 | 93,532 | 84,652 | 48,793 | 31,162 | 1,352,807 |
| 1992-93 | 16,460 | 7,150 | 50 | 56 | 4,000 | 3,874 | - | - | 31,590 |
| 1993-94 | 26,100 | 24,075 | 2,349 | 280 | 2,440 | 5,716 | - | - | 60,960 |
| 1994-95 | 39,000 | 37,600 | 9,920 | 3,080 | 3,240 | 5,540 | - | - | 98,380 |
| 1995-96 | 27,000 | 32,200 | 8,000 | 1,040 | - | 4,140 | - | - | 72,380 |
| 1996-97 | 26,800 | 24,300 | 6,960 | 3,160 | - | 4,360 | - | - | 65,580 |
| 1997-98 | 22,200 | 20,500 | 4,320 | 4,340 | 820 | 4,660 | - | - | 56,840 |
| 1998-99 | 32,400 | 18,900 | 7,480 | 7,180 | 5,740 | 5,920 | - | - | 77,620 |
| 1999-00 | 64,000 | 23,200 | 15,930 | 10,700 | 7,080 | 6,210 | - | - | 127,120 |
| 2000-01 | 31,600 | 16,000 | 8,760 | 9,660 | 7,320 | 7 ,300 |
- | - | 80,640 |
| 2001-02 | 67,200 | 37,400 | 27,080 | 18,020 | 11,520 | 10,680 | - | - | 171,900 |
| 2002-03 | 48,000 | 23,300 | 9,640 | 4,780 | 4,680 | 5,020 | - | - | 95,420 |
| Total | 796,720 | 584,405 | 318,114 | 223,599 | 140,372 | 148,072 | 48,793 | 31,162 | 2,291,237 |
Table 6: Circulating coin production 2002-03
| Denomination | Design | Date of Coin | Alloy | Pieces (millions) |
| 5 cents | Standard | 2002 | Cupro-Nickel | 80.252 |
| 5 cents | Standard | 2003 | Cupro-Nickel | 52.178 |
| 10 cents | Standard | 2002 | Cupro-Nickel | 44.089 |
| 10 cents | Standard | 2003 | Cupro-Nickel | 9.137 |
| 20 cents | Standard | 2002 | Cupro-Nickel | 21.523 |
| 50 cents | CoF1 | 2001 | Cupro-Nickel | 0.080 |
| 50 cents | Outback | 2002 | Cupro-Nickel | 11.507 |
| 50 cents | Volunteers | 2003 | Cupro-Nickel | 5.725 |
| 1 Dollar | Outback | 2002 | Aluminium Bronze | 16.025 |
| 2 Dollars | Standard | 2002 | Aluminium Bronze | 14.099 |
| Total | 254.615 |
(1) Centenary of Federation
Table 7: Visitor numbers
| 1998-99 | 1999-00 | 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | |
| Total visitor numbers | 146,101 | 173,198 | 186,597 | 208,429 | 182,104 |
Production figures for proof and special coins, medal, medallions and circulating coin for other countries are available on the Mint website at
Customer service charter
The Mint's customer service charter is available in hard copy and on its website. The Customer service charter is due to be reviewed in December 2003.
Customer complaints are managed within the context of the Mint's overall Quality Management System that meets with the ISO9001-2000 Quality System certification. The complaints are dealt with according to the Australian Standard AS 4269-19951 Complaints Handling. Relevant staff are trained in all aspects of customer service.
The Mint carries out market research to establish customer satisfaction levels as well as views about the coins it is planning to issue, either through surveys or focus groups. Mint staff also regularly meet collectors. The Mint we
bsite hosts a forum for the public to comment on or discuss numismatic matters and it provides the Mint with direct feedback on many matters. In addition the public can raise matters directly with the Mint through letters, phone calls, emails and two dedicated email response addresses on the Mint's website.
Corporate services
Corporate Services Division assists in the achievement of Treasury's outcomes through the provision of accurate, cost effective and timely management of information, corporate services, and advice to the department and Treasury ministers. The division also seeks to provide a quality-working environment for Treasury staff.
Services provided by Corporate Services Division include information technology, information and records management, information technology training, publishing, web page and other communications support, ministerial liaison, human resource management, financial and accounting services, and contracting and facilities management.
Key priorities in 2002-03
The priorities identified for Corporate Services Division in the 2002-03 Corporate Plan were to:
- finalise the review of the Chief Executive's Instructions;
- continue developing human resource information and management systems;
- continue improving budgeting and financial management, including upgrading Treasury's Financial Management Information System (FMIS);
- progress the implementation of the Knowledge and Information Management Framework:
- commence phased implementation of electronic records management;
- upgrade IT operating systems to Windows 2000 and Microsoft Office XP;
- replace desktop IT equipment and Local Area Network infrastructure;
- develop and deliver training programs to support Treasury projects and systems;
- further develop online Internet services;
- contribute to the negotiation of Treasury's third Certified Agreement, including further refinements to the Performance Management System; and
- improve contract management and procurement policies and procedures.
Key outcomes in 2002-03
Outcomes relating to the above priorities are as follows:
- Treasury's Chief Executive Instructions were rewritten in 2002-03 to reflect Government best practice standards as determined by the Australian National Audit Office (ANAO) and Department of Finance and Administration. Staff have access to the Chief Executive Instructions on the intranet, and staff training should raise awareness of the Chief Executive Instructions.
- Staff access to personal and professional information using Aurion Employee Self-Service has been improved. The Employee Self-Service system enables staff to have 24-hour access to personal records, pay details, leave balances and training courses. In August 2003 the Performance Appraisals and Curriculum Vitae modules in the Aurion system were released, enabling employees and managers to complete all performance appraisal processes, including their professional curricula vitae, online.
- Treasury's FMIS (SAP R/3) was upgraded to version 4.6 on 31 March 2003. The upgrade provides a range of additional functionality and improved reporting. As part of the upgrade project, staff were provided with targeted training and updated user documentation.
- The core layer of the Information and Knowledge Management framework is Treasury's systems and information sources. The emphasis was on implementing TRIM electronic records management system and migrating IT systems to a common platform.
- The progressive implementation of TRIM electronic records management commenced in May 2002. Corporate Services Division and several policy areas have implemented TRIM electronic records management. Full implementation will take 12 to 18 months as successful implementation depends on Treasury staff adopting effective change management practices.
- IT systems upgrades included SAP R/3, Aurion and the ministerial correspondence system. New business systems development included the Balance of Payments system, the Foreign Investment system and Contracts Management system.
- Treasury's desktop and laptop computers, printers, network servers, storage and backup facilities were upgraded. Treasury has a standard and consistent technical platform which provides cost and performance benefits.
- The Treasury Intranet Stage III development commenced in March 2003 and is due for release in November 2003. The project involves redeveloping the current intranet and will include a new interface, improved and faster retrieval of data, a restructuring of information and the inclusion of a content management system for content administrators.
- Treasury uses the Internet as its primary mechanism to disseminate information to the public. In 2002-03, 6,339 emails were received through the Treasury and ministerial websites, compared with 2,587 in 2001-02. Five new websites were released in 2002-03 to assist with the consultation process for public reviews undertaken by Treasury.
- A departmental training calendar was developed during 2002-03 combining professional, information technology, SAP and electronic records, training schedules. The training calendar is linked to departmental seminars and specialised training provided by the policy groups. The calendar provides a central point to access information on internally-delivered training and development opportunities.
- The Australian Industrial Relations Commission certified Treasury's third Certified Agreement on 10 September 2002, following negotiation with employees. The Certified Agreement is to run for two years and its accompanying new pay model introduces more flexible salary arrangements for Australian Public Service Level 6 (APS6), Executive Level 1 (EL1) and Executive Level 2, (EL2) level staff.
- In 2002-03 the Performance Management System was reviewed. Amendments included redefining role accountabilities, developing the Treasury organisational management principles and refining the performance appraisal processes.
- Treasury completed a review of its contract management and procurement policies in 2002-03 to better align Treasury policies with the ANAO Contract Management Better Practice Guide. The review included revision of standard contract documentation and development and implementation of a contract risk management framework. Awareness of contract management and procurement responsibilities is raised through training seminars.
Other key outcomes in 2002-03 for Corporate Services Division included:
- The appointment of a new internal auditor, a revision in the composition of the Treasury Audit Committee (including the appointment of an external member), and refocus of the internal audit plan to concentrate more on key business activities and risks. These measures were designed to strengthen the audit function.
- The introduction of a more rigorous quality assurance control framework for Treasury's financial statement's and reporting processes.
- The development of a performance monitoring framework based on the balanced scorecard approach to more effectively evaluate divisional performance.
- Assistance in integrating some 100 additional staff into the department following the transfer of the tax law design function from the Australian Taxation Office to Treasury.