6.1 Introduction
This chapter provides information on all Australian Government tax expenditures. Details include a description of the tax expenditure, its commencement date and (where applicable) its expiry date, legislative references for the tax expenditure and estimates of the annual benefit derived by the recipients of the tax expenditure.
Tax expenditures are grouped according to the benchmark against which they are estimated and by functional categories. The table below provides details of how this chapter is organised.
| Benchmark | Specific benchmark category | Functional category | TES reference code |
| INCOME TAX (A - E) |
Personal income (A)7 | General public services | A1 – A7 |
| Defence | A8 – A16 | ||
| Education | A17 | ||
| Health | A18 – A24 | ||
| Tax concessions for certain taxpayers | A25 – A35 | ||
| Certain government income support payments | A36 – A45 | ||
| Housing and community amenities | A46 – A47 | ||
| Recreation and culture | A48 | ||
| Other economic affairs | A49 – A53 | ||
| Substantiation provisions for employment-related expenses | A54 – A56 | ||
| Miscellaneous | A57 – A65 | ||
| Business income (B)8 | General public services | B1 | |
| Health | B2 – B3 | ||
| Social security and welfare | B4 – B7 | ||
| Tax concessions for certain taxpayers | B8 | ||
| Recreation and culture | B9 – B12 | ||
| Other economic affairs | B13 – B23 | ||
| Capital expenditure, effective life and depreciation | B24 – B57 | ||
| Prepayments and advance expenditures | B58 – B62 | ||
| International tax expenditures | B63 – B80 | ||
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | B81 – B89 | ||
| Manufacturing and mining | B90 – B92 | ||
| Miscellaneous | B93 – B98 | ||
| Retirement savings (C) | C1 – C8 | ||
| Fringe benefits tax (D) | General public services | D1 | |
| Defence | D2 – D4 | ||
| Education | D5 – D6 | ||
| Health | D7 – D8 | ||
| Social security and welfare | D9 – D14 | ||
| Housing and community amenities | D15 – D16 | ||
| Other economic affairs | D17 – D27 | ||
| Transport and communications | D28 – D30 | ||
| Miscellaneous | D31 – D49 | ||
| Capital gains tax (E) | E1 – E22 | ||
| COMMODITY (F) | Consumption taxes | Fuel | F1 – F6 |
| Tobacco | F7 – F8 | ||
| Alcohol | F9 – F18 | ||
| Motor vehicles | F19 | ||
| General consumption | F20 – F21 | ||
| NATURAL RESOURCE TAXES (G) | Petroleum | G1 |
The descriptions of tax expenditures included in this chapter present a range of information about each identified tax expenditure item. The following example illustrates the information included for each tax expenditure.
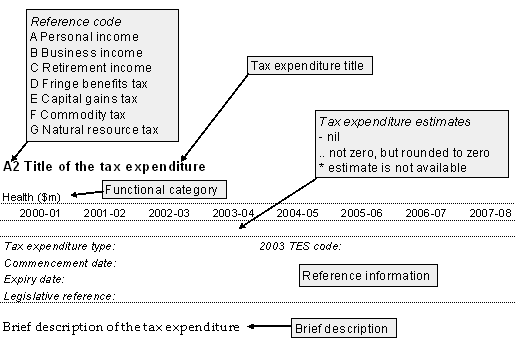
The reference information provides details of:
|
The ‘type of tax expenditure’ in the reference information classifies tax expenditures according to the way in which they are delivered, for instance, by way of a tax exemption, tax deduction, tax offset, concessional tax rate or deferral of a tax liability.
In the case of fringe benefits tax, tax expenditures may also be delivered through a reduction in taxable value, discounted valuation or record keeping exemption. A reduction in taxable value is a tax expenditure that arises where the taxable value of the fringe benefit is reduced by some factor. A discounted valuation describes provisions where a valuation other than the actual value of the benefit is used as a basis for calculating the tax. Record keeping exemptions arise where an employer is not obliged to maintain current records of benefits to calculate the tax.
Certain tax expenditures relating to depreciation allow for the accelerated write-off of depreciable assets and these tax expenditures are identified as accelerated write-off. In the early years of an asset’s life, accelerated write-offs allow larger deductions than the benchmark depreciation treatment. In the later years of an asset’s life when the accelerated write-off is complete, deductions that would be allowed under the benchmark are no longer available. Thus, accelerated write-offs act like tax deferrals.
6.2 Income tax benchmark
Personal income
Tax expenditures for general public services
A1 Exemption of official salaries and certain other income of the Governor-General and Governor of any State
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A1
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- No longer available for appointments after 28 June 2001
- Legislative reference:
- Section 51-15 ITAA97
The ordinary and statutory income of the Governor-General and State Governors derived from a source outside Australia, along with their official salaries, were exempt from income tax. This exemption is not available for appointments made after 28June2001.
A2 Deduction for expenses incurred by election candidates
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A2
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985 (local government provisions introduced in 1985)
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 25-60 ITAA97
Certain expenses incurred by candidates contesting federal, state and territory government elections are deductible. Expenses of up to $1,000 per election incurred by candidates contesting local government elections are also deductible. Candidates are eligible for the deduction irrespective of whether they successfully contest the election.
For further details see the ATO web site www.ato.gov.au or Taxation Ruling TR1999/10.
A3 Exemption of official salary and emoluments of officials of prescribed international organisations
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A3
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- International Organisations (Privileges and Immunities) Act 1963
The official salary and emoluments of officials of prescribed international organisations may be exempt from income tax as part of the privileges and immunities required under the terms of certain international agreements. Prescribed international organisations include the United Nations organisations, the OECD, the International Court of Justice and the International Atomic Energy Agency.
For further details see Taxation Ruling TR 92/14.
A4 Exemption of income of certain visitors to Australia
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A4
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 23(b), 23(c)(iii), 23(c)(iv), 23(c)(v) and 23(v) ITAA36
The earnings of certain non-residents and visitors to Australia are exempt from income tax.
This exemption generally includes income earned by non-residents:
- for provision of expert advice to the Australian Government or State Governments;
- in an official capacity by visiting foreign government representatives;
- for conducting research or attending conferences of behalf of educational scientific or philanthropic societies;
- for overseas press coverage of events relating to the visit of a non-resident referred to in one of the preceding points; or
- for provision of advice to the A
ustralian Government regarding Australia’s defence (subject to approval by the Treasurer).
A5 Exemption of income earned by Australians working on approved overseas projects
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 240 | 330 | 450 | 460 | 500 | 550 | 610 | 680 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A5
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 23AF ITAA36
Note: estimates include tax expenditures A5 and A6.
Income earned by Australians working overseas on certain approved projects for a continuous period of 91 days or more may be exempt from income tax. To be approved, projects must be considered to be in the national interest by the Minister for Trade (or the Minister’s delegate).
A6 Exemption of income earned by Australians working in a foreign country
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Included in A5
|
||||||||
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A6
- Commencement date:
- 1986
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 23AG ITAA36
Foreign earnings derived while engaged in foreign service for a continuous period of 91 days or more may be exempt from income tax. This exemption does not apply where the foreign earnings are exempt from income tax in the foreign country for certain reasons.
A7 Exemption from income tax and Medicare levy of residents of Norfolk Island
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 11 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A7
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 24G and Section 251U ITAA36
Income earned by residents of Norfolk Island is exempt from income tax and Medicare levy.
Tax expenditures for defence
A8 Exemption of pay and allowances for part-time Australian Defence Force Reserve personnel
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A8
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 51-5 ITAA97
The pay and allowances of part-time Australian Defence Force Reserve personnel are exempt from income tax.
A9 Exemption of certain allowances and bounties and the value of certain rations and quarters to Australian Defence Force personnel
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A9
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 51-5 ITAA97
Certain allowances and bounties payable to Australian Defence Force personnel are exempt from income tax. These include the following allowances — separation, living-out, living-away-from-home, child-education, scholarship, retention-of-lodging, disturbance, transfer and deployment allowances — and re-engagement bounties.
In the case of living-away-from-home allowances and living allowances paid to Australian Defence Force personnel, the benchmark treatment is compensation for the actual additional cost faced by employees in living away from their homes. Accordingly, this tax expenditure relates solely to that part of the allowance that is in excess of this compensation.
The market value of rations and quarters supplied without charge to Australian Defence Force personnel is exempt from income tax.
A10 Exemption of pay and allowances earned in Australia by foreign forces
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A10
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
Section 23(u) ITAA36
Pay and allowances earned in Australia by foreign forces are exempt from income tax. This does not apply if the Australian Government makes the payment.
A11 Exemption of compensation for loss of pay and allowances paid to Australian Defence Force Reserve personnel
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A11
- Commencement date:
- 1996
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 51-33 ITAA97
Australian Defence Force Reserve personnel who are forced to resign due to injuries sustained whilst employed by the Reserves may receive compensation for the loss of pay and allowances. Such compensation payments are exempt from income tax. This exemption, legislated in 2003, applies to assessments for the 1996-97 and later income years.
A12 Exemption of compensation for loss of deployment allowance paid to Australian Defence Force members
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A12
- Commencement date:
- 1996
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 51-32 ITAA97
Australian Defence Force personnel may receive compensation for the loss of deployment allowance where the deployment allowance ceases to be paid upon repatriation to Australia due to injuries sustained in a warlike situation. Such compensation payments are exempt from income tax. This exemption, legislated in 2003, applies to assessments for the 1996-97 and later income years.
A13 Exemption of pay and allowances earned by members of the Australian Defence Force in operational areas
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A13
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 23AC and 23AD ITAA36
Pay and allowances made to Australian Defence Force personnel during a period of service in an operational area are exempt from income tax.
Estimates from 2000-01 reflect ongoing deployment of Australian Defence Force personnel to East Timor. Other recent increases result from operations in the Middle East, Afghanistan and the Solomon Islands.
A14 Exemption of some payments to Australian Federal Police and civilian personnel in service with an armed force of the United Nations
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A14
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 23AB(5), 23AB(10) and 23AB(6) ITAA36
Australian Federal Police and civilian personnel contributed by Australia to an armed force of the United Nations may receive compensation in respect of death, impairment or incapacity resulting from their service. Such compensation payments are exempt from income tax. The estate of a deceased civilian who has performed United Nations service may also receive relief from unpaid tax in respect of pay and allowances. Furthermore, a partial income tax exemption applies to living allowances paid to civilians who died during periods of United Nations service.
A15 Tax offsets for Australian Defence Force personnel serving overseas and for Australian Federal Police and civilians serving with United Nations forces
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Included in A46
|
||||||||
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A15
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 79B ITAA36 and Section 23AB(7) ITAA36
Australian Defence Forces personnel who serve overseas and civilian personnel contributed by Australia to an armed force of the United Nations may be eligible for a tax offset. Personnel or civilians qualify for the full offset amount if their total period of overseas service is more than half the income year or if they die while on service. Personnel or civilians who serve for less than half the income year receive a proportion of the full amount. The offset is made up of a base amount with additional entitlements for individuals who maintain dependants.
A16 Exemption from the Medicare levy for Australian Defence Force members and their relatives and associates
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 40 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A16
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 251U ITAA36
Income earned by Australian Defence Forces personnel (or relatives of, or individuals otherwise associated with, Australian Defence Force personnel) is exempt from the Medicare levy.
Tax expenditures for education
A17 Exemption of income from certain educational scholarships or similar forms of assistance
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A17
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 23(ya) ITAA36 and Section 51-10 ITAA97
Income derived by way of scholarships, bursaries or other educational allowances to a student receiving full-time education at a school, college or university may be exempt from income tax. Income derived as part of an Australian Government scheme to assist secondary education or the education of isolated children is exempt from income tax, excluding federal education or training payments or education entry payments provided under the Social Security Act 1991.
Income derived by way of scholarships, allowances, bursaries or other education allowances provided by the Australian Government to an overseas student may also be exempt from income tax.
Finally, grants from the Australian-American Educational Foundation (that is, Fulbright Scholarships) are exempt if they are from funds made available to the Foundation under the agreement establishing it.
Tax expenditures for health
A18 Medical expenses tax offset
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 150 | 185 | 220 | 240 | 280 | 330 | 380 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A18
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 159P ITAA36
A tax offset is available to a taxpayer whose net medical expenses in the income year exceed a certain threshold. Qualifying medical expenses may relate both to resident taxpayers and any resident dependants but are net of available reimbursements, such as Medicare and private health insurance refunds. Currently, the value of the offset is 20 per cent of the excess of medical expenses above a threshold of $1,500.
A19 Exemption from the Medicare levy for residents with a taxable income below a threshold
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 310 | 340 | 360 | 370 | 370 | 370 | 370 | 370 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A19
- Commencement date:
- 1986
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 7 of the Medicare Levy Act 1986
The Medicare levy generally applies at a flat rate to a taxpayer’s whole taxable income. Residents whose taxable income falls below a threshold are exempt from the Medicare levy, with the levy phased in once the taxpayer’s income exceeds the threshold.
A20 Medicare levy exemption for non-residents, repatriation beneficiaries and foreign government representatives
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A20
- Commencement date:
- 1986
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 251U ITAA36
The income of non-residents, repatriation beneficiaries and foreign government representatives is exempt from the Medicare levy.
A21 Tax offset for private health insurance
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 195 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A21
- Commencement date:
- 1997, amended in 1999
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 61-300 to 61-345 ITAA97
A tax offset is available for holders of appropriate private health insurance cover. The offset is worth 30 per cent of the value of the insurance premium. This offset can be claimed as a refundable tax offset, a direct payment or through reduced premiums.
Prior to 2001-02 the component claimed as a refundable tax offset was recorded as a tax expenditure. Since 2001-02 all claims (direct payments and tax offsets) have been recorded in Budget documentation as an expense and so are not recorded in the Tax Expenditures Statement.
A22 Exemption of 30 per cent private health insurance refund, including expense equivalent
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 470 | 590 | 670 | 740 | 750 | 790 | 830 | 870 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A22
- Commencement date:
- 1998
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 52-125 ITAA97
Taxpayers can receive a 30 per cent refund on the costs of private health insurance either as a refundable tax offset, direct payment or through reduced premiums. These payments are exempt from income tax.
A23 Medicare levy surcharge on high-income earners who do not hold private health insurance
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -150 | -95 | -115 | -145 | -145 | -145 | -145 | -145 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Increased rate
- 2003 TES code:
- A23
- Commencement date:
- 1997
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 8B-8D of the Medicare Levy Act 1986
Individuals and couples who do not have private health insurance and whose income exceeds a threshold are subject to an increased Medicare levy. The Medicare levy surcharge of 1 per cent is payable by single individuals with total taxable income and reportable fringe benefits in excess of $50,000 and couples and families with combined taxable income and reportable fringe benefits in excess of $100,000. The surcharge has applied since 1 July 1997 and is treated as a negative tax expenditure.
A24 Deduction for payment of United Medical Protection Limited support payments
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - | .. | .. | 1 | 1 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A24
- Commencement date:
- 2003
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 25-105 ITAA97
From 2003-04, a specific tax deduction is available for all medical practitioners (including retirees) who are required to pay United Medical Protection Limited (UMP) support payments, equal to the full amount of the payment. UMP support payments are required of medical practitioners to fund the Australian Government’s assumption of certain medical indemnity liabilities from medical defence organisations.
Tax concessions for certain taxpayers
A25 Tax offset for sole parents
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A25
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Replaced in 2000
- Legislative reference:
- Section 159K ITAA36
A sole parent who had the sole care of a student or a dependant child under 16 was eligible for a tax offset until it was replaced with Family Tax Benefit, Part B on 1July2000.
A26 Tax offsets for taxpayers supporting a parent, parent-in-law, or invalid relative
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A26
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 159J ITAA36
A taxpayer who contributes to the maintenance of one or more dependants may be entitled to a tax offset. Dependants must be Australian residents and be either an invalid relative or a parent (or pant-in-law).
These offsets are indexed annually to the consumer price index.
A27 Tax offset for recipients of certain social security benefits, pensions or allowances
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-0 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 890 | 940 | 1,020 | 1,060 | 1,100 | 1,140 | 1,180 | 1,230 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A27
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 160AAA ITAA36
Taxpayers who receive certain social security benefits, pensions or allowances may be eligible for a tax offset (the beneficiary or the pensioner tax offsets). Qualifying government payments include:
- various income support payments (for example, Newstart or sickness allowance);
- various pensions (for example, age pension (where not eligible for the Senior Australians’ Tax Offset) and carer payment);
- Australian Government education and training payments (for example, youth allowance); and
- various other payments (for example, payments to Community Development Employment Project (CDEP) participants and exceptional circumstances relief payments).
A28 Senior Australians' Tax Offset
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,490 | 1,580 | 1,630 | 1,630 | 1,680 | 1,730 | 1,780 | 1,830 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A28
- Commencement date:
- 1996
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 160AAAA and 160AAAB ITAA36
The Senior Australians’ Tax Offset (SATO) may be available to taxpayers who are eligible to receive the age pension or a veterans’ benefit, pension or allowance. This includes individuals who qualify for but do not receive a benefit (for example, because they do not meet the means testing criteria).
A29 Tax offsets for dependant spouse, child-housekeeper and housekeeper who cares for a prescribed dependant
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 360 | 340 | 340 | 340 | 340 | 340 | 350 | 350 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A29
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 159J and 159L ITAA36
A taxpayer may be entitled to claim one of the following tax offsets:
- a tax offset for the maintenance of a dependent spouse where there are no dependent children;
- a tax offset for the maintenance of a child-housekeeper, where a dependent spouse is not maintained and neither the taxpayer nor the taxpayer’s spouse is eligible for Family Tax Benefit Part B; or
- a tax offset for the maintenance of a housekeeper caring for one or more dependants, where a dependent spouse is not maintained and neither the taxpayer nor the taxpayer’s spouse is eligible for Family Tax Benefit Part B.
These tax offsets are indexed annually to the consumer price index.
A30 Tax offset for low income earners
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 460 | 410 | 400 | 390 | 680 | 650 | 630 | 610 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A30
- Commencement date:
- 1993
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 159N ITAA36
A taxpayer whose taxable income falls below a threshold is eligible for the low income tax offset of $235. This amount decreases at a rate of four cents for each dollar above $21,600. Prior to 2003-04, the maximum offset was $150, and reduced at incomes above $20,700.
A31 Family Tax Benefit, Parts A and B
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A32
- Commencement date:
- 2000
- Expiry date:
- A New Tax System (Family Assistance) Act 1999
- A New Tax System (Family Assistance) Act 1999
The Family Tax Benefit can be claimed as either a direct payment or through the tax system as a refundable tax offset. From 2001-02 all claims are recorded in Budget documentation as an expense. Prior to 2001-02 the component that was claimed as a tax offset was recorded in the Tax Expenditures Statement as a tax expenditure.
A32 Release from particular tax liabilities in cases of serious hardship
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A33
- Commencement date:
- Introduc
ed before 1985 - Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Division 340 of Schedule 1 to the Tax Administration Act 1953 (formerly section 265 of ITAA36, which was repealed from 1 September 2003)
An individual taxpayer can be released from a tax liability where payment of the liability would cause serious hardship. This release from tax liability acts like a tax exemption. Prior to 1 September 2003, the release arrangements applied principally to tax assessments and did not apply to taxpayers paying on an instalment basis. The procedures under which an individual taxpayer can be released from a tax liability were streamlined from 1 September 2003. In addition, the scope of relief was broadened to include Pay As You Go instalments and fringe benefits tax instalments. The streamlining of these procedures was undertaken to increase the efficiency and flexibility of the system for taxpayers to seek relief from tax debts.
A33 Deduction for tax agent fees for family tax benefit claims lodged through Centrelink
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | .. | - | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A34
- Commencement date:
- 2003
- Expiry date:
- 2004
- Legislative reference:
- Section 25-8 ITAA97
A tax deduction will be available for tax agent fees for family tax benefit claims relating to the 2001-02 income year lodged through Centrelink between 1 July 2003 and 30 June 2004.
Claims made in 2003-04 relating to the 2001-02 income year can only be lodged through Centrelink, not the Australian Taxation Office.
A34 Mature Age Worker Tax Offset
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - | - | 390 | 415 | 415 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- New
- Commencement date:
- 2004
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Not yet legislated
Workers aged 55 years and over may be entitled to a tax offset, based on the amount of their earned income. The offset applies from the 2004-05 income year. A maximum offset amount of $500 is payable on assessment.
A35 Tax rebate for child care
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - | - | - | 280 | 305 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- New
- Commencement date:
- 2004
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Not yet legislated
Taxpayers who receive Child Care Benefit (CCB) for approved child care that meets the CCB work/study/training test may be eligible for a 30 per cent rebate for out of pocket expenses. The rebate will be claimed on the succeeding year’s tax return. This means that the rebate entitlement for the 2004-05 year will be claimed in the return for the 2005-06 year.
Tax exemptions for certain government income support payments
A36 Exemption of certain income support benefits, pensions or allowances
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 880 | 900 | 930 | 960 | 1,100 | 1,080 | 1,160 | 1,200 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A35
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 52-5 to 52-40 ITAA97
Certain social security pensions, benefits and allowances and certain repatriation pensions paid under the Social Security Act 1991 and the National Health Act 1953 are exempt from income tax.
A37 Exemption of Family Tax Benefit, Parts A and B, including expense equivalent
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,980 | 2,600 | 2,550 | 3,130 | 2,730 | 3,020 | 3,110 | 3,180 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A36
- Commencement date:
- 2000
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 52-150 ITAA97
Taxpayers can receive the Family Tax Benefit either as a direct payment or as a refundable tax offset. Payments are exempt from income tax regardless of delivery method.
A38 Exemption of rent subsidy payments under the Commonwealth/State mortgage and rent relief schemes
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A37
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 51-30 ITAA97
Rent subsidy payments received by renters and paid under the Mortgage and Rent Relief Scheme by an Australian Government agency are exempt from income tax.
A39 Exemption of Child Care Benefit
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 330 | 450 | 480 | 470 | 530 | 550 | 560 | 570 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A38
- Commencement date:
- 2000
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 52-150 ITAA97
Child Care Benefit paid by the Australian Government is exempt from income tax.
The Child Care Benefit can be paid directly to child care service providers to reduce the fees charged. Alternatively, the payment can be made directly to parents as a lump sum at the end of the income year.
A40 Exemption of one-off payments to senior Australians
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 540 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A39
- Commencement date:
- 2000, 2001
- Expiry date:
- 2001
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 52-10 and 59-5 ITAA97
The Aged Persons Savings Bonus and the Self-Funded Retirees Supplementary Bonus made to senior Australians under the A New Tax System (Bonuses for Older Australians) Act 1999 were exempt from income tax. Claims had to be lodged by 30 June 2001. Also exempt from income tax was the $300 one-off payment provided to people of age pension age who received income support or were outside the taxation and income support system, as announced in the 2001-02 Budget. Claims through Centrelink had to be made by 31 December 2001.
These payments and the associated tax expenditure are one-off in nature.
A41 Exemption of Utilities Allowance and Seniors Concession Allowance
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - | - | 15 | 25 | 25 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- New
- Commencement date:
- 2004
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Not yet legislated - expected to be included in sections 52-10 and 52-65 ITAA97
Utilities Allowances and Seniors Concession Allowances payable to senior Australians are exempt from income tax.
A Utilities Allowance of $100 per year for singles and couples is paid to Australians of age pension age receiving income support, while a Seniors Concession Allowance of $200 per year is paid to self-funded retirees with a Commonwealth Seniors Health Card.
A42 Exemption of the Baby Bonus
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | 8 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 15 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A40
- Commencement date:
- 2002
- Expiry date:
- Claims can be made for children born prior to 30 June 2004
- Legislative reference:
- Subdivision 61-I ITAA97
Baby bonus payments are exempt from income tax. The Baby Bonus is available to parents who gained legal responsibility for a child between 1 July 2001 and 30 June 2004. Payments are expected to continue for some years at around the 2004-05 level before tapering off.
A43 Exemption of certain war-related payments and pensions
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 370 | 380 | 410 | 420 | 440 | 470 | 490 | 520 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A41
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 52-60 to 52-110 ITAA97
Note: estimates include tax expenditures A43 and A44.
Repatriation pensions, or pensions, allowances and payments of a similar nature, and certain war-related payments and pensions are exempt from income tax.
A44 Exemption of certain pensions, annuities or allowances paid for persecution
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Included in A43 | ||||||||
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A42
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 23(kc), 23(kca) and 23AL ITAA36
From 2001-02, certain foreign source World War II payments are exempt from income tax. This applies where the payment is in connection with:
- any wrong or injury;
- loss of, or damage to, property; or
- any other detriment;
suffered as a result of:
- persecution by an enemy of the Commonwealth, or enemy-associated regime, during World War II;
- flight from such persecution; or
- participation in a resistance movement against such forces.
Prior to 2001-02, certain pensions, annuities and allowances paid by the Federal Republic of Germany and the Kingdom of the Netherlands, as compensation for persecution or disability arising during World War II, were exempt from income tax.
A45 Income tax exemption for certain pensions received by residents of Papua New Guinea
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A43
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 23(kd) ITAA36
Pensions received from Australia by Papua New Guinea residents are exempt from income tax providing Papua New Guinea has a reciprocal exemption in place.
Tax expenditures for housing and community amenities
A46 Zone tax offsets
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 175 | 175 | 180 | 185 | 185 | 190 | 195 | 195 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A44
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 79A ITAA36
Note: estimates include tax expenditures A15 and A46.
Taxpayers who live in prescribed remote areas of Australia are eligible for a tax offset.
For further information about the zone offset, see Tax Ruling TR 94/27.
A47 Exemption of payments made under the First Home Owners Grant Scheme
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 330 | 450 | 290 | 250 | 240 | 250 | 250 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A45
- Commencement date:
- 2000
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- A New Tax System (Commonwealth-State Financial Arrangements) Act 1999 - Appendix D, Intergovernmental Agreement on Commonwealth-State Financial Relations, Appropriation Act (No. 2) 2001-02 (for the additional grant) and relevant state legislation
Payments made under the First Home Owners Grant Scheme are exempt from tax. Eligible applicants purchasing or building their first home from 1 July 2000 are entitled to $7,000 assistance to offset the impact of the GST. For first home owners who entered into contracts between 9 March 2001 and 31 December 2001, the Australian Government funded an additional $7,000 grant and between 1 January and 30June2002 funded an additional $3,000 grant to build or purchase new and previously unoccupied homes.
Tax expenditures for recreation and culture
A48 Income averaging for authors, inventors, performing artists, production associates and sportspersons
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Concessional rate
- 2003 TES code:
- A46
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Division 405 ITAA97
Authors (including composers and artists), inventors, performing artists, production associates and sportspersons can be subject to significant fluctuations in their income. These taxpayers may be eligible for an income averaging scheme that provides concessional rates of tax for abnormal receipts above average income.
Tax expenditures for other economic affairs
A49 Deductibility of union dues and subscriptions to business associations
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A47
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 25-55 ITAA97
Union dues and subscriptions to trade, business or professional associations are specifically tax deductible up to a maximum amount of $42. This deduction is available in addition to any work-related expense deduction.
For further information on this deduction, see Tax Determination 1999/45.
A50 Deferral of tax and exemption for share discounts on qualifying employee share acquisition schemes
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deferral, exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A48
- Commencement date:
- 1995
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 26AAC and Division 13A ITAA36
Discounts on shares (or rights to acquire shares) acquired under an employee share acquisition scheme are generally included in the taxpayer’s assessable income in the year in which the share or right was acquired. However, a taxpayer may defer the inclusion of discounts on qualifying shares or rights for up to 10 years. Alternatively, the taxpayer may elect to bring the discount on qualifying shares or rights to assessment in the year of acquisition and benefit from an exemption on the first $1,000. These concessions only apply under certain conditions and in particular, the share or right must be acquired after 28 March 1995 (Division 13A). Certain other shares or rights are eligible for an exemption on the first $200 of the discount (Section 26AAC).
A51 Tax deferral advantage arising from return of after-tax contributions to a pension or annuity
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deferral
- 2003 TES code:
- A49
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 27H ITAA36
The value of a pension or annuity may partly consist of contributions towards the income stream from the recipient’s after-tax income. This part of the income stream is not taxed again when it is returned in the form of pension or annuity payments. A tax expenditure arises because the tax-free part of a pension or annuity is apportioned evenly over the term of the income stream, providing a tax deferral advantage.
A52 Increased tax rates for certain minors
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | -6 | -6 | -6 | -6 | -6 | -6 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Increased rate
- 2003 TES code:
- A50
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Division 6AA ITAA36
Higher rates of taxation apply to the ‘unearned income’ of certain minors. ’Unearned income’ includes dividend, interest, rent, royalties and other income from property. The special rates do not apply to minors classed as being in a full-time occupation.
A53 Part-year tax-free threshold
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -10 | -9 | -9 | -10 | -10 | -10 | -10 | -10 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Increased rate
- 2003 TES code:
- A51
- Commencement date:
- 1986
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 16 to 20 of the Income Tax Rates Act 1986
Students who cease full-time education for the first time receive a pro-rated tax-free threshold, corresponding to the number of months that the student is not enrolled in full-time education. Taxpayers who become an Australian resident for the first time or cease to be an Australian resident also receive a pro-rated tax-free threshold. This corresponds to the number of months that the taxpayer is an Australian resident.
Concessions under the substantiation provisions for employment-related expenses
A54 A reasonable overtime meal allowance
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A52
- Commencement date:
- 1987
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section
900-60 ITAA97
A taxpayer is able to claim a deduction for a ‘reasonable’ overtime meal allowance expense payable under an industrial instrument.
For further information about the value of a reasonable overtime meal, see Tax Ruling TR 2002/12.
A55 Certain travel expenses in and outside Australia
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A53
- Commencement date:
- 1987
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 900-50 and 900-55 ITAA97
A taxpayer is able to claim a deduction in relation to a travel allowance for reasonable expenses on accommodation, meals and incidental costs of travel in Australia, and meals and incidental costs of travel outside Australia.
For further information about the value of a reasonable domestic travel allowance, see Tax Ruling TR 2002/12.
A56 Alternatives to the logbook method of substantiating car expenses
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A54
- Commencement date:
- 1987
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 900-70 and 900-75 ITAA97
Three alternative methods to the logbook method (which is based on actual expenditure) are available to value car expense deductions:
- the one-third of actual expenses method (only available if business use exceeds 5,000 kilometres);
- the 12 per cent of original value method (only available if business use exceeds 5,000 kilometres); and
- the cents per kilometre method (only available up to a maximum of 5,000 business kilometres).
Miscellaneous tax expenditures
A57 Tax offset on certain payments of income received in arrears
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A55
- Commencement date:
- 1986
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Sections 159ZR-159ZRD ITAA36
Individual taxpayers that receive lump sum payments of certain income that accrued in earlier income years may be entitled to a tax offset. Income that qualifies for the tax offset includes certain back payments of salary or wages, lump sum payments of workers or accident compensation, and social security and other benefits, received on or after 1 July 1986.
A58 Deduction for gifts to approved donees
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 310 | 340 | 390 | 420 | 450 | 490 | 540 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A56
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Division 30 ITAA97
Note: includes tax expenditures A58 and A59.
Gifts of cash and property (subject to certain conditions) of a value of $2 or more to certain approved recipients are tax deductible. Eligible recipients are listed in tables in Subdivision 30-B of the ITAA97.
A59 Deduction for contributions with an associated minor benefit
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Included in A58 | ||||||||
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- New
- Commencement date:
- July 2004
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Division 30 ITAA97
Individual taxpayers may claim an income tax deduction for the net amount of contributions made to a deductible gift recipient where the taxpayer receives an associated minor benefit (subject to certain conditions). The deduction available is the contribution less the market value of the minor benefit.
A60 Deduction for contributions to prescribed private funds
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code
: - New
- Commencement date:
- 2001
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Division 30 ITAA97 and regulations to the ITAA97
Prescribed private funds allow businesses, families and individuals to establish and donate to a charitable trust of their own, for the purposes of disbursing funds to a range of other deductible gift recipients. Complying funds are prescribed in regulations under the Income Tax Assessment Act 1997.
Donations of $2 or more to approved prescribed private funds are tax deductible.
A61 Exemption of post-judgment interest awards in personal injury compensation cases
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A57
- Commencement date:
- 1992
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 51-57 ITAA97
Interest may accrue on a judgment debt arising in personal injury compensation cases relating to the period between the original judgment and when the judgment is finalised. Such interest is exempt from tax.
The provisions, introduced in 1999-2000, apply to compensation paid in the 1992-93 and later income years.
A62 Tax offset of interest on certain government securities
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Offset
- 2003 TES code:
- A58
- Commencement date:
- Introduced before 1985
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 160AB ITAA36
Taxpayers are entitled to a tax offset equal to 10 cents for each dollar of interest on certain government or semi-government securities issued before 1 November 1968.
A63 Exemption from income tax of one-off payments to former civilian internees and detainees of the Japanese
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A59
- Commencement date:
- 2001
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 11 of the Compensation (Japanese Internment) Act 2001
The one off ex-gratia payment of $25,000 made in 2001 to former civilian internees and detainees of the Japanese in compensation for their pain and suffering in World War II is exempt from income tax. This is a one-off tax expenditure, reflecting the nature of these payments.
A64 Exemption for structured settlements and structured orders
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Exemption
- 2003 TES code:
- A60
- Commencement date:
- 2001
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Section 54 ITAA97
Certain annuities provided to personal injury victims under structured settlements and structured orders are exempt from income tax. These provisions allow personal injury victims who would be eligible to receive large tax-free lump sum compensation payments to receive all or part of their compensation in the form of a tax-free annuity or annuities.
A65 Immediate deduction for low-value depreciating assets not used in business
| 2000-01 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
- Tax expenditure type:
- Deduction
- 2003 TES code:
- A61
- Commencement date:
- 2001
- Expiry date:
- Legislative reference:
- Subsection 40-80(2) ITAA97
An immediate deduction is available for depreciating assets costing less than $300 where those assets are used predominantly for the purpose of producing assessable income and where that income is not income from carrying on a business.
7 Personal income tax expenditures are generally grouped according to their functional group. However, tax expenditures that relate to employment-related expenses are grouped separately.
8 Business income tax expenditures are generally grouped according to their functional group. However, tax expenditures that relate to capital expenditures, prepayments and international taxation have been grouped separately. In addition, business income tax expenditures for agriculture, forestry and fishing are also reported under ‘Tax expenditures relating to capital expenditure, effective life and deprecia
tion’.